Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 10
10 W/cm
W/cm
Skobelev, I. Yu.*; Ryazantsev, S. N.*; Kulikov, R. K.*; Sedov, M. V.*; Filippov, E. D.*; Pikuz, S. A.*; Asai, Takafumi*; Kanasaki, Masato*; Yamauchi, Tomoya*; Jinno, Satoshi; et al.
Photonics (Internet), 10(11), p.1250_1 - 1250_11, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Optics)It is challenging to clearly distinguish the impacts of the optical field and collisional ionization in the evolution of the charge state of a plasma produced when matter interacts with high-intensity laser pulses. In this work, time-dependent calculations of plasma kinetics are used to show that it is possible only when low-density gaseous targets with sufficiently small clusters are used. In the case of Ar plasma, the upper limit of the cluster radius was estimated to be 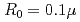 m.
m.
Nagayama, Shota; Harada, Hiroyuki; Shimogawa, Tetsushi*; Sato, Atsushi*; Yamada, Ippei; Chimura, Motoki; Kojima, Kunihiro; Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu
Proceedings of 20th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.526 - 530, 2023/11
We have been developing "Non-destructive electrostatic septum" for a slow extraction. This septum has multiple electrodes placed around the region without the beam hitting and separate the beam by its electric field. To evaluate its electric field, we have built a prototype septum and a test machine, which consists of an electron gun and monitors. This test machine can measure the electric field indirectly by using a narrow electron beam. The experiment results of prototype septum is good agreement with the calculation one. However, this electric field distribution is not enough to separate the beam. A step function-like electric field distribution is ideal for the beam separation with minimal negative effect on the beam. We have studied to improve the electrode configuration to match the beam shape. In this paper, we present the result of the electric field measurements and the septum improvement. Additionally, we describe the future plan of this development.
Nagayama, Shota; Harada, Hiroyuki; Shimogawa, Tetsushi*; Yamada, Ippei; Chimura, Motoki; Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.503 - 507, 2023/01
Synchrotron accelerators realize physics experiments and radiation cancer treatment using the slow extraction technique, in which beams are stored in the ring and gradually delivered. We have devised and are currently developing a "non-destructive electrostatic septum" based on a new method, which in principle cannot be solved by conventional methods and is a cause of equipment failure and output limitation. It is ideal to generate a force distribution similar to a staircase function with discontinuous gaps at the boundary. In this presentation, we will show the calculation method for optimizing the electrode and wire configuration to generate a Lorentz force with a distribution similar to a staircase function in vacuum, and the calculation results of the beam breakup due to the generated Lorentz force. The compact proof-of-principle machine developed for the ongoing demonstration of this method will also be introduced.
Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Iwashita, Yoshihisa*
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 32(6), p.4006705_1 - 4006705_5, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Space charge compensation technique using multipole magnetic field components has been proposed to transport high intensity beam in the J-PARC linac. In order to realize this compensation technique, a compact size permanent hybrid multi-pole magnet would be suitable. A magnet system for the simultaneous production of quadrupole and adjustable octupole components using permanent magnet materials and have manufactured a first model of the magnet systems.
Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Moriya, Katsuhiro; Takayanagi, Tomohiro
Proceedings of 31st International Linear Accelerator Conference (LINAC 2022) (Internet), p.364 - 367, 2022/09
MEBT1 (Medium Energy Beam Transport 1) of the J-PARC LINAC is a 3 MeV beam transport system located between the RFQ (Radio Frequency Quadrupole) and DTL (Drift Tube Linac). In the MEBT1, the beam-optical matching for injection into DLT and chopping for injection into acceleration phase of 3 GeV synchrotron, located downstream to the LINAC, are performed. The characteristics of MEBT1 are an important factor in determining the beam quality in the J-PARC accelerator facility. To achieve beam power of 1 MW and beyond, improving the stability and reliability of MEBT1 is an important development issue. The application of permanent magnets to the beam focusing system to the MEBT1 is under consideration to achieve improved stability and reliability. In this presentation, we report the design of focusing magnets using permanent magnet material and the results of the lattice study of MEBT1 with permanent magnets.
Hojo, Tomohiko*; Shibayama, Yuki; Ajita, Saya*; Koyama, Motomichi*; Akiyama, Eiji*
Materia, 61(7), p.413 - 418, 2022/07
no abstracts in English
Chimura, Motoki; Harada, Hiroyuki; Kinsho, Michikazu
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2022(6), p.063G01_1 - 063G01_26, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:28(Physics, Multidisciplinary)In the low-energy region of a high-intensity ion linac, a strong space-charge field causes a rapid beam emittance growth over a short distance of only few meters. The beam emittance growth leads to a beam loss and the machine activation raising a serious issue for regular maintenance of the accelerator component and beam power ramp up. In this work, we studied the mechanism of beam emittance growth due to the space-charge field based on three-dimensional particle-tracking simulation and theoretical considerations. Numerical simulations done for the high-intensity linac at J-PARC shows that the nonlinear terms in the space-charge field directly cause a beam emittance growth and beam halo formation. Then, we also propose a method to mitigate the beam emittance growth by using an octupole magnetic field, which arises as one of the nonlinear terms in the space-charge field. By applying this method in the simulation, we have succeeded mitigating the beam emittance growth.
Yano, Yasuhide; Hashidate, Ryuta; Tanno, Takashi; Imagawa, Yuya; Kato, Shoichi; Onizawa, Takashi; Ito, Chikara; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Otsuka, Satoshi; Kaito, Takeji
JAEA-Data/Code 2021-015, 64 Pages, 2022/01
From a view point of practical application of fast breeder reactor cycles, which takes advantage of safety and economic efficiency and makes a contribution of volume reduction and mitigation of degree of harmfulness of high-level radioactive waste, it is necessary to develop fuel cladding materials for fast reactors (FRs) in order to achieve high-burnup. Oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) steel have been studied for use as potential fuel cladding materials in FRs owing to their excellent resistance to swelling and their high-temperature strength in Japan Atomic Energy Agency. It is very important to establish the materials strength standard in order to apply ODS steels as a fuel cladding. Therefore, it is necessary to acquire the mechanical properties such as tensile, creep rupture strength tests and so on. In this study, tensile and creep rupture strengths of 9Cr-ODS steel claddings were evaluated using by acquired these data. Because of the phase transformation temperature of 9Cr-ODS steel, temperature range for the evaluation was divided into two ones at AC1 transformation temperature of 850 C.
C.
Takeda, Masayasu
Bunseki, 2021(11), p.611 - 615, 2021/11
no abstracts in English
Hayashi, Naoki; Hatakeyama, Shuichiro; Fukuta, Shimpei*
Proceedings of 18th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.679 - 682, 2021/10
In order to achieve a high availability in a user facility accelerator complex, it is necessary to understand in detail not only the simple failure cause of the magnet or the acceleration cavity power supply, but also complex interlocked events. At J-PARC, not only the primary interlock information but also the data recorded by the beam diagnostic system before the interlocked event is used to carefully reconstruct the event and clarify the cause more accurately. This time, we proceeded with the analysis based on more detailed waveform of the RCS Beam Loss Monitor and the events during simultaneous operation of MLF and MR. We present various events of the beam destination switching problem, the influence of the ion source discharged, and the events related to the RCS extraction kicker.
Aihara, Jun; Kuroda, Masatoshi*; Tachibana, Yukio
Proceedings of 28th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 28) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2021/08
To maintain the structural integrity of fuel elements for a high-temperature gas-cooled reactor (HTGR) under disaster conditions, strong and oxidation-resistant fuel elements should be further developed. The HTGR fuel elements employ a hot-pressed silicon carbide (SiC)/carbon (C) mixed matrix to improve the oxidative resistance. Hot-press conditions such as pressure, temperature, and duration would be one of the factors that affect the strength of the HTGR fuel elements. To identify the optimal hot-press conditions for preparing the high-strength fuel elements, modelling their effects on the mechanical-strength properties of the HTGR fuel elements should be evaluated quantitatively. In this study, the response surface model, which represents the relationship between the hot-press conditions and the mechanical-strength properties, has been constructed by introducing statistical design-of-experiment approaches.
Harada, Hiroyuki; Saha, P. K.; Kinsho, Michikazu
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011028_1 - 011028_6, 2021/03
Recently, humankind had big discovery about neutron star, which is great big nuclear in the space. They are discovery of neutron star with twice mass of solar in 2010 and detection of gravity wave when two neutron stars incorporate in 2017. In order to understand the high dense matter like the neutron star, project of experimental researches by using accelerated heavy ion beams are planed in the world. The J-PARC facility consists of three accelerators, which are 400 MeV linac, 3 GeV rapid cycling synchrotron and Main Ring synchrotron. The accelerated MW class high intensity proton beams are used in many experiments. We have simulation study of the heavy ion beam in J-PARC to fully utilize high intensity ability of J-PARC. We propose the accelerator scheme of the beam in J-PARC and the intensity will reach to the world record. In my talk, I will introduce the accelerator scheme for the high-intensity heavy ion beam in J-PARC.
Harada, Hiroyuki; Saha, P. K.; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*; Fuchi, Aoi*; Sato, Atsushi*; Kinsho, Michikazu
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011026_1 - 011026_6, 2021/03
The charge-exchange multi-turn injection by using a carbon stripper foil is adopted in high-intensity proton ring accelerators worldwide. It is a beneficial method to compress the pulsed proton beam with high intensity but there are serious issues for high intensity. First issue is a short lifetime of the foil by deformation or breaking itself. Another issue is high radiation dose corresponding to the scattered particles on the foil. Therefore, a non-destructive stripping injection method is required for higher intensity proton beam. We newly propose a non-destructive method of H stripping by using only laser. The new method is called "laser stripping injection". To establish our method, we are preparing for a POP (Proof-of-Principle) experiment of 400 MeV H- stripping to proton at J-PARC. In our presentation we will present the current status of laser system development for laser stripping injection at J-PARC.
stripping by using only laser. The new method is called "laser stripping injection". To establish our method, we are preparing for a POP (Proof-of-Principle) experiment of 400 MeV H- stripping to proton at J-PARC. In our presentation we will present the current status of laser system development for laser stripping injection at J-PARC.
Harada, Hiroyuki; Hayashi, Naoki
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011027_1 - 011027_6, 2021/03
The transverse betatron tune is one of the most important key parameters in a ring accelerator because emittance growth and beam loss occur directly in case of crossing a betatron resonance. Especially, the tune must be required a controll with high accuracy in high intensity proton accelerator from the view point of space charge force and the beam instability. In general measurement method, the betatron tune is measured by analyzing the detected beam oscillation on Fourier transform. However, the beam is quickly accelerated and the revolution frequency of the beam changes quickly in a rapid cycling synchrotron. So, the tune accuracy is not improved. A new method was developed for high resolution analysis of the tune and was evaluated in J-PARC accelerator. Tune accuracy was successfully improved from 0.013 to less than 0.001. Tune controll with high accuracy is base for high-intensity beam. In this paper, the new method is introduced and the measured result in J-PARC is report.
Hotchi, Hideaki; Harada, Hiroyuki; Hayashi, Naoki; Kinsho, Michikazu; Okabe, Kota; Saha, P. K.; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Kazami; Yamamoto, Masanobu; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011018_1 - 011018_6, 2021/03
no abstracts in English
Hayashi, Naoki; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Hatakeyama, Shuichiro*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011017_1 - 011017_6, 2021/03
The J-PARC Rapid-Cycling Synchrotron (RCS) is designed as an 1-MW high intensity proton accelerator. Beam intensity diagnostics is an important device to prove the accelerator performance. The RCS has two instruments based on different principles, namely Direct-current Current Transformer (DCCT) and Slow-CT (SCT). It was realized that SCT showed strange behavior when continuous 1-MW demonstration had been performed, although there were no problem under 1-MW equivalent operation with single shot. The origin of the problem seems to be limited band width at higher frequency and asymmetric circulating beam current pattern. On the other hand, DCCT also showed output signal saturation with 1.2-MW equivalent single shot. But, SCT worked properly with this conditions. These problems have to be solved for future continuous 1-MW and higher intensity operation. On this presentation, we will show beam and test pulse data and discuss about how to measure these problems.
Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Nakanoya, Takamitsu; Yamazaki, Yoshio; Saha, P. K.; Kinsho, Michikazu; Yamamoto, Shunya*; Okazaki, Hiroyuki*; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*; Yamada, Naoto*; Yamagata, Ryohei*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011019_1 - 011019_7, 2021/03
The multi-turn charge-exchange H beam injection scheme with stripper foils is one of the key techniques to achieve a MW-class high power proton beam. The J-PARC RCS adopts Hybrid type Boron-doped Carbon (HBC) stripper foil, which was developed in KEK to improve the lifetime. Indeed, the RCS user operation confirmed that HBC foil has the great advantage of a longer lifetime against high beam irradiation. To examine characteristics of the HBC foils, various beam studies were performed, such as the stripping efficiency measurement and long-term observation with an H
beam injection scheme with stripper foils is one of the key techniques to achieve a MW-class high power proton beam. The J-PARC RCS adopts Hybrid type Boron-doped Carbon (HBC) stripper foil, which was developed in KEK to improve the lifetime. Indeed, the RCS user operation confirmed that HBC foil has the great advantage of a longer lifetime against high beam irradiation. To examine characteristics of the HBC foils, various beam studies were performed, such as the stripping efficiency measurement and long-term observation with an H beam in the J-PARC RCS, foil analysis using RBS, EDR and PIXE methods, and SEM and TEM observation after the ion beam irradiation in Takasaki Ion Accelerators for Advanced Radiation Application (TIARA) on National Institutes for Quantum and Radiological Science and Technology (QST). Recently, the deposition apparatus for the HBC foils from the KEK Tsukuba-site was relocated to the JAEA Tokai-site, and we started fabrication of new HBC foil in 2017. (The new one fabricated in JAEA we call J-HBC foil.) And, we continue investigations in TIARA with the J-HBC foils. Furthermore, in-depth researches by changing the process parameters of the foil deposition are carried on. Recent results suggest that the amount of the boron doped in the foil is more important parameter than the ratio of the discharge amount of carbon from cathode and anode electrodes. In this presentation, we will report the details of recent analysis of the J-HBC foil.
beam in the J-PARC RCS, foil analysis using RBS, EDR and PIXE methods, and SEM and TEM observation after the ion beam irradiation in Takasaki Ion Accelerators for Advanced Radiation Application (TIARA) on National Institutes for Quantum and Radiological Science and Technology (QST). Recently, the deposition apparatus for the HBC foils from the KEK Tsukuba-site was relocated to the JAEA Tokai-site, and we started fabrication of new HBC foil in 2017. (The new one fabricated in JAEA we call J-HBC foil.) And, we continue investigations in TIARA with the J-HBC foils. Furthermore, in-depth researches by changing the process parameters of the foil deposition are carried on. Recent results suggest that the amount of the boron doped in the foil is more important parameter than the ratio of the discharge amount of carbon from cathode and anode electrodes. In this presentation, we will report the details of recent analysis of the J-HBC foil.
Okabe, Kota; Liu, Y.*; Otani, Masashi*; Moriya, Katsuhiro; Shibata, Takanori*; Chimura, Motoki*; Hirano, Koichiro; Oguri, Hidetomo; Kinsho, Michikazu
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011011_1 - 011011_6, 2021/03
To realize more stable operation of the J-PARC accelerators, we have a re-design plan of an MEBT1 (Medium Energy Beam Transport). At the J-PARC Linac, the MEBT1 has transverse and longitudinal beam matching section for the DTLs. However there are some locally activated spots in DTL area at the current beam power level. To reduce beam loss during a beam acceleration at the DTLs is a most important task for a stable user operation. The first thing we should do is investigation a connection between beam quality in the MEBT1 and parameters of the upstream hardware. In this presentation, we will report a high intensity beam study results at the MEBT1.
Nakashima, Hiroshi
JAEA-Conf 2020-001, p.69 - 74, 2020/12
J-PARC (Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex) is a high-energy proton accelerator complex of the world's highest beam power. Because of its very high beam power and its high energy as well as the large-scale accelerator complex, we encountered some very difficult problems on radiation safety design. Various examinations and countermeasures were considered in order to overcome the difficulty. This paper introduces some of them. In addition, some new knowledge obtained during 10 years after completion are described.
Hosoya, Yoshihiro*; Matsumura, Yuta*; Tomota, Yo*; Onuki, Yusuke*; Harjo, S.
ISIJ International, 60(9), p.2097 - 2106, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:31.59(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)